Divide And Conquer Practice Problems
Data Construction and Algorithms Class
Practice Problems on Divide and Conquer
Recent Articles on Divide and Conquer
What is Divide and Conquer?
Divide and Conquer is an algorithmic epitome in which the trouble is solved using the Split, Conquer, and Combine strategy.
A typical Divide and Conquer algorithm solves a trouble using following three steps:
- Separate: This involves dividing the trouble into smaller sub-problems.
- Conquer: Solve sub-problems by calling recursively until solved.
- Combine: Combine the sub-problems to become the last solution of the whole problem.
Standard algorithms that follow Divide and Conquer algorithm
The following are some standard algorithms that follow Divide and Conquer algorithm.
- Quicksort is a sorting algorithm. The algorithm picks a pivot element and rearranges the array elements so that all elements smaller than the picked pivot element move to the left side of the pivot, and all greater elements move to the right side. Finally, the algorithm recursively sorts the subarrays on the left and right of the pivot element.
- Merge Sort is also a sorting algorithm. The algorithm divides the assortment into two halves, recursively sorts them, and finally merges the ii sorted halves.
- Closest Pair of Points The problem is to find the closest pair of points in a prepare of points in the x-y aeroplane. The problem tin exist solved in O(n^two) time by calculating the distances of every pair of points and comparing the distances to find the minimum. The Divide and Conquer algorithm solves the problem in O(N log N) fourth dimension.
- Strassen's Algorithm is an efficient algorithm to multiply two matrices. A simple method to multiply two matrices needs 3 nested loops and is O(n^iii). Strassen's algorithm multiplies 2 matrices in O(n^2.8974) time.
- Cooley–Tukey Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm is the most common algorithm for FFT. It is a carve up and conquer algorithm which works in O(N log N) fourth dimension.
- Karatsuba algorithm for fast multiplication does the multiplication of two due north-digit numbers in at most
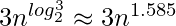 single-digit multiplications in full general (and exactly
single-digit multiplications in full general (and exactly when northward is a ability of 2). It is, therefore, faster than the classical algorithm, which requires n 2 unmarried-digit products. If n = 210 = 1024, in detail, the exact counts are threeten = 59, 049 and (ii10)2 = 1, 048, 576, respectively.
when northward is a ability of 2). It is, therefore, faster than the classical algorithm, which requires n 2 unmarried-digit products. If n = 210 = 1024, in detail, the exact counts are threeten = 59, 049 and (ii10)2 = 1, 048, 576, respectively.
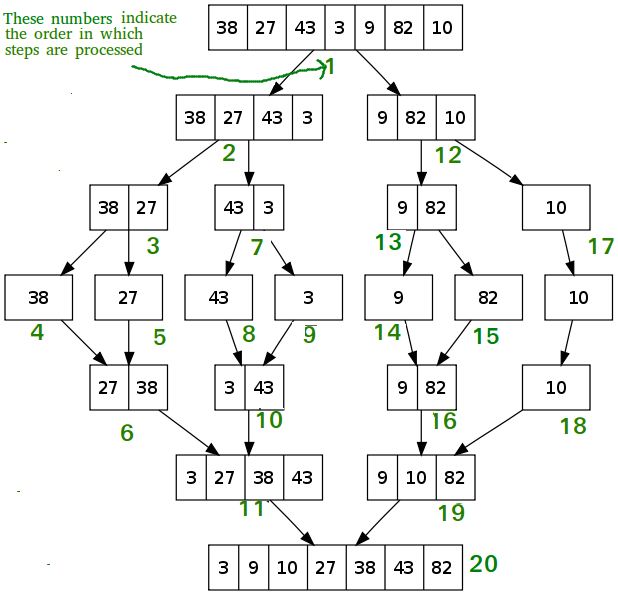
Example of Separate and Conquer algorithm
A classic example of Separate and Conquer is Merge Sort demonstrated below. In Merge Sort, we divide assortment into two halves, sort the ii halves recursively, and then merge the sorted halves.
Topics :
- Standard Algorithms
- Binary Search Based
- Misc
- Quick Links
Standard Algorithms :
- Intoduction to Separate and Conquer
- Binary Search
- Randomized Binary Search Algorithm
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Tiling Trouble
- Count Inversions
- Summate pow(ten, due north)
- Closest Pair of Points
- Closest Pair of Points | O(nlogn) Implementation
- Multiply two polynomials
- Strassen's Matrix Multiplication
- The Skyline Problem
- Maximum Subarray Sum
- Longest Mutual Prefix
- Search in a Row-wise and Cavalcade-wise Sorted 2D Array
- Karatsuba algorithm for fast multiplication
- Convex Hull (Simple Divide and Conquer Algorithm)
- Quickhull Algorithm for Convex Hull
- Distinct elements in subarray using Mo's Algorithm
Binary Search Based :
- Median of 2 sorted arrays
- Median of two sorted arrays of different sizes
- Floor in a Sorted Array
- Find closest number in array
- Find a Stock-still Signal in a given arrray
- Find a superlative element in a given assortment
- Check for Majority Chemical element in a sorted array
- 1000-thursday Element of Two Sorted Arrays
- Detect the Rotation Count in Rotated Sorted array
- Find the minimum chemical element in a sorted and rotated array
- Find the only repeating element in a sorted assortment of size n
- Discover alphabetize of an actress chemical element present in one sorted array
- Find the element that appears one time in a sorted array
- Count number of occurrences (or frequency) in a sorted array
- Observe the maximum element in an assortment which is first increasing and so decreasing
- Subtract and Conquer
- Binary Search using pthread
- Binary Search on Singly Linked List
- The painter's partition problem
- The painter's partition problem | Set up 2
- Observe the number of zeroes
- Numbers whose factorials end with n zeros
- Observe the missing number in Arithmetic Progression
- Number of days after which tank will become empty
- Find bitonic point in given bitonic sequence
- Detect the point where a monotonically increasing part becomes positive first time
Misc :
- Iterative Tower of Hanoi
- Program for Tower of Hanoi
- Foursquare root of an integer
- Discover cubic root of a number
- Allocate minimum number of pages
- Collect all coins in minimum number of steps
- Modular Exponentiation (Power in Modular Arithmetic)
- Find a peak element in a 2D array
- Program to count number of set bits in an (large) array
- Maximum and minimum of an array using minimum number of comparisons
- Find frequency of each element in a limited range array in less than O(northward) time
- Minimum deviation between adjacent elements of array which comprise elements from each row of a matrix
- Search element in a sorted matrix
- Piece of cake manner to think Strassen's Matrix Equation
- Largest Rectangular Area in a Histogram | Set 1
- Advanced master theorem for divide and conquer recurrences
- Identify k elements such that minimum distance is maximized
- Iterative Fast Fourier Transformation for polynomial multiplication
- Write you own Power without using multiplication(*) and division(/) operators
- Sequences of given length where every element is more than than or equal to twice of previous
- Shuffle 2n integers in format {a1, b1, a2, b2, a3, b3, ……, an, bn} without using actress space
Quick Links :
- 'Practice Bug' on Divide and Conquer
- 'Quizzes' on Divide and Conquer
If yous like GeeksforGeeks and would similar to contribute, you can also write an article and mail service your commodity to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if yous discover anything wrong, or y'all want to share more than data about the topic discussed to a higher place.
Start Your Coding Journey Now!
Divide And Conquer Practice Problems,
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/divide-and-conquer/
Posted by: steinmetzocas1943.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Divide And Conquer Practice Problems"
Post a Comment