Is It Better To Add Cart Items In Databse Or Use Session
An e-commerce shopping cart serves as a virtual cart that allows customers to add and hold items until they consummate the purchase. It accepts payments of customers and organizes and distributes all order information to the merchant, customer, and other relevant parties.
This process requires a database to store and think the relevant data while supporting the functionality of the shopping cart. A shopping cart database will contain all the disquisitional information about products, orders, and customers and let users to perform real-time changes reflected in their shopping sessions. The database tin have immutable structures or a split up table to store all the lodge details.
Note: The purpose of this post is to present considerations for designing a shopping cart database. It'due south non a pace-by-step tutorial for building a production-set up cart database as we accept done to power our order management system and cart APIs.
Designing the Database
A shopping cart database should be highly available, fault-tolerant, and highly responsive to provide customers with a shine shopping experience 24/7. When designing a shopping cart database, it can be divided into three main components for better categorization and understanding of the underlying data structure:
- Static Data
- Session Data
- Candy Information
Static Data
This component will include somewhat static information that the customer needs only to recall while interacting with a shopping cart. The data is stored in the following types of tables:
-
producttable -
discounttable -
usertable
Session Data
This is the most important component of the shopping cart database where all the live interactions (session details) are stored when the client is interacting with the shopping cart.
-
shopping_sessiontable -
cart_itemtable
Processed Data
Once the customer completes a transaction, we need to permanently store the order information by moving the Session Data into permanent storage. Additionally, nosotros need to shop the payment details.
-
order_detailstable -
order_itemstabular array -
payment_detailstable
Tabular array Relationships in Database
The following diagram demonstrates the relationships within the to a higher place-mentioned tables inside the database using a sample fieldset. The fields in the tables may depend on the requirements of the specific e-commerce platform and tin can range from a simple to complex listing of fields.
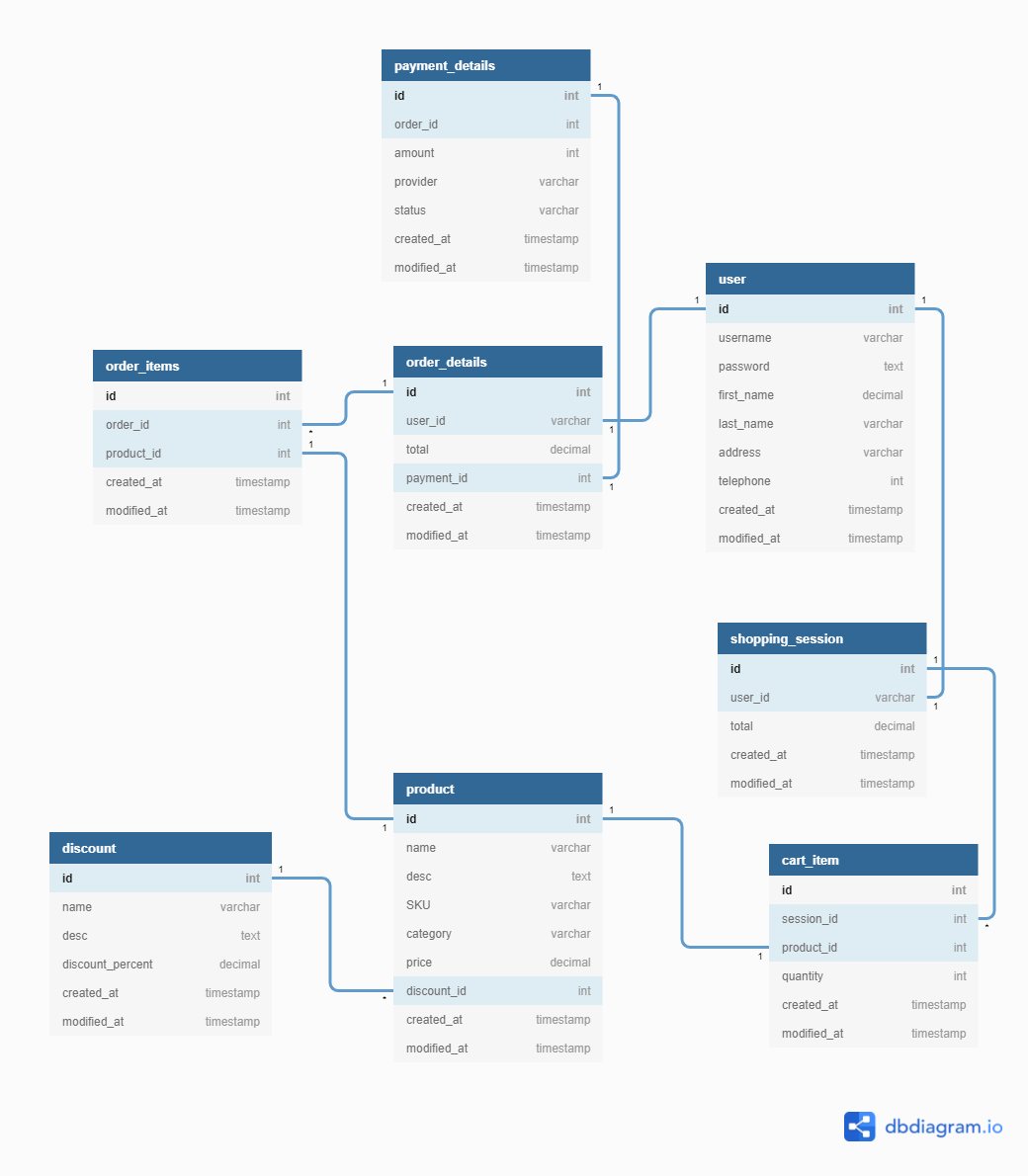
When designing the database, we need to have a good balance betwixt simplicity and roofing the required functionality. Let's dig a bit deeper into the structure of the shopping cart database.
Static information component
In a shopping cart, tables like product and discount are only required to reference the production, inventory, and pricing details. They will only get SELECT queries when a customer adds an item to the shopping cart. The only fourth dimension the product tabular array gets updated is when a purchase is completed and needs to update the inventory of the products (UPDATE statement). Regular updates for these tables are made past the administrators of the east-commerce platform and should exist a part of the product information management (PIM) system.
The user table is but needed in the shopping cart to link the orders and sessions with the registered users. This allows the eastward-commerce platform to map the orders with the relevant users. The user details table is updated but when a new user is created, or when a user updates their details. This functionality is out of the scope of the shopping cart. Within the shopping cart, we only map the order/session with the user.
Since nosotros only recall the data and limit write queries to update inventory, the product table is considered a static data component in the shopping cart. Hither is an example of a production table:
CREATE TABLE `shopping_cart`.`product` ( `id` INT(10) Not NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `proper name` VARCHAR(100) Non NULL, `desc` TEXT Not NULL, `SKU` VARCHAR(fifty) Not NULL, `category` VARCHAR(50) NOT Zilch, `cost` DECIMAL(six) NOT NULL, `discount_id` INT(five) DEFAULT '0', `created_at` TIMESTAMP NOT Zip, `modified_at` TIMESTAMP, UNIQUE Key `prod_index` (`id`) USING BTREE, UNIQUE KEY `sku_index` (`id`,`SKU`) USING BTREE, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), CONSTRAINT `fk_prod_discount` Strange KEY (`discount_id`) REFERENCES `shopping_cart`.`disbelieve` (`id`) ON DELETE Prepare NULL ON UPDATE Ready NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB; Session data
This component contains the highly active tables within the database, facilitating the real-time functionalities of the shopping cart. The purpose of the shopping_session and cart_item tables are to act as highly efficient and temporary storage to support the live interactions of a client with the shopping cart. When a customer visits the eastward-commerce platform, a session is created (shopping_session), and each item added to the cart is captured in the cart_item tabular array linked to the specific session.
This enables us to capture the country of the shopping cart regardless of the client interactions in the e-commerce platform. Combining these details with website cookies enables u.s. to provide previous shopping cart details even if the customer navigates out of the eastward-commerce platform.
A considerable architectural effort is required to streamline these tables to support all kinds of alive queries (SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE) made to the database without hindering the user experience. This data fix also allows the retailers to sympathise any inefficiencies in their shopping experience past identifying the behavioral patterns of the customers.
For example, if some customers are dropping out at the payment phase, the platform developers can drill downwardly and identify any issues with the payment processing.
Hither is an instance of a shopping_session table:
CREATE TABLE `shopping_cart`.`shopping_session` ( `id` INT(30) Non Cypher AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` INT(10) DEFAULT NULL, `total` DECIMAL(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0.00', `created_at` TIMESTAMP Not Cipher, `modified_at` TIMESTAMP, UNIQUE KEY `session_index` (`id`,`user_id`) USING BTREE, Chief KEY (`id`), CONSTRAINT `fk_shopping_user` FOREIGN Fundamental (`user_id`) REFERENCES `shopping_cart`.`user` (`id`) ON DELETE Prepare Zip ON UPDATE Set NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB; Processed data
The processed information contains the completed order details with the associated payment details. When a transaction is completed, nosotros motility the relevant data set from the shopping_session to order_details table and cart_item to order_item tabular array and delete those records from the shopping_session and cart_item tables as they are no longer needed.
We can utilise a unmarried table group (shopping_session/cart_item or order_details/cart_item) with an actress field (due east.grand. order_status) to betoken whether the order has been completed. However, this will create a bloated data set and negatively impact the performance of the e-commerce platform.
By separating the information into ii distinct groups, we can keep track of the completed society in a separate table. This method allows maintaining the history of the orders while reducing the load of the shopping_session and cart_item tables to only contain information that needs to facilitate live interactions.
The combination of order_details and the order_item tables with the payment_details table creates the consummate order details and enables the e-commerce platform to arrange the mail service-processing and distribution of the products or services.
Another advantage of the processed information component is that information technology can be used for analytics purposes. Matching the data with relevant users of the e-commerce platform enables u.s. to provide suggestions based on previous purchases and carry out targeted marketing campaigns.
Here is an example of an order_details table:
CREATE TABLE `order_details` ( `id` INT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` INT(10), `full` DECIMAL(10) NOT Nothing, `payment_id` INT(20) Non Cypher, `created_at` TIMESTAMP NOT Cypher, `modified_at` TIMESTAMP, UNIQUE KEY `order_index` (`id`) USING BTREE, UNIQUE KEY `customer_order_index` (`id`,`user_id`) USING BTREE, Principal KEY (`id`), CONSTRAINT `fk_shopping_user_order` FOREIGN Key (`user_id`) REFERENCES `shopping_cart`.`user` (`id`) ON DELETE Gear up NULL ON UPDATE Gear up NULL, CONSTRAINT `fk_order_payment` Foreign KEY (`payment_id`) REFERENCES `shopping_cart`.`payment_details` (`id`) ON DELETE Prepare NULL ON UPDATE SET NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB; Expanding the Scope of the Database
Shopping cart databases are only a single function of a vast e-commerce experience. This section will briefly explain how to extend the database to cover additional functionalities past introducing new tables and fields to the existing database.
User details
A user table can be extended with other tables such as user_address and user_payment to shop user preferences. Thus, it enables a polish shopping experience past providing the stored details of the user for a faster checkout process.

Product details
Combining additional tables like inventory and category to the products table enables u.s. to expand the functionality of product direction. This is a primal consideration when expanding the e-commerce platform to integrate PIM functionalities.
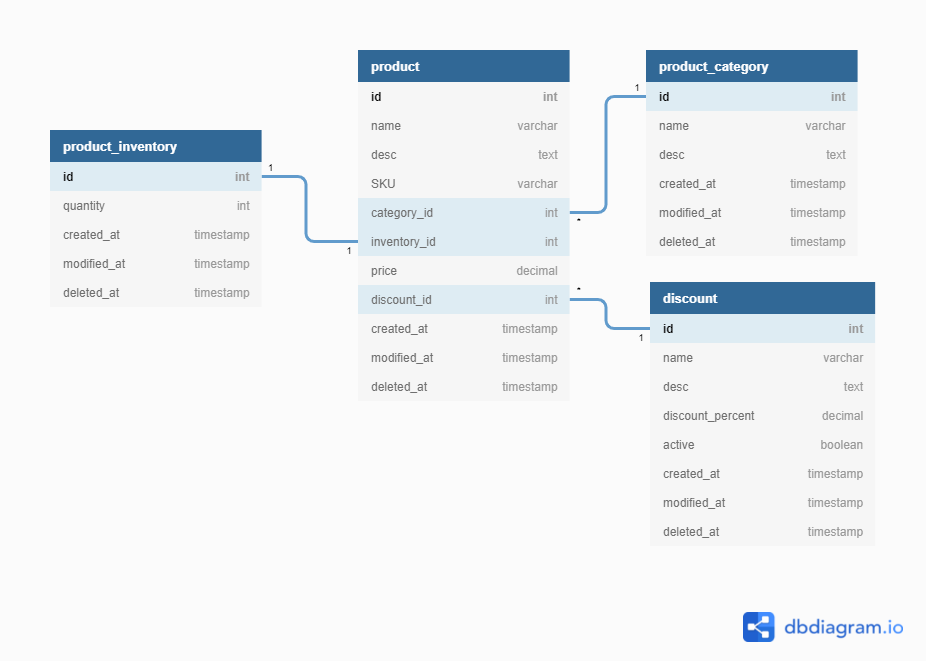
A shopping cart database can exist extended farther to support any requirement. The database tin can human action equally a standalone database powering the complete eastward-commerce platform or a function of a database cluster focused on shopping cart functionality. The possibilities are express simply by the development attempt and the user requirements.
In all instances, information technology is advisable to decouple the tables and create split tables other than creating a few large tables. This increases the flexibility and the overall performance of the database while reducing data redundancy.
Equally an additional notation, it'southward a expert idea to plan a reliable backup and disaster recovery strategy to the database from the initial deployment of the database. It volition increment the resilience of the database and offer peace of mind to the platform administrators.
Lodge direction software (OMS) provides everything needed to receive, track, and fulfill customer orders online. These solutions expose the shopping cart database through an API and allow e-commerce platform administrators to ensure that all order and inventory data is up to date.
OMS software also comes with shopping cart APIs that add flexibility to the shopping experience by enabling customers to edit their cart, apply promotional codes, and specify shipping and billing information. For instance, a user can use PATCH /cart/{cartId}/items to change their cart, and the API endpoint is designed to ensure the cart is upwards to appointment at whatever given signal. Below, y'all can meet two sample requests for a registered and guest user.
Registered User (Logged in User)
{ "cartId": 604638499041, "userAuthToken": "half-dozen^[e-mail protected]!0lT3rxb02d7&", "registeredUser": true, "items": [ { "itemId": "1000000122", "quantity": 2, "group": [ "5e31a1f9fcc2b500089c10e8" ], "price": { "sale": 0, "base": 120, "discount": { "price": 0 }, "currency": "USD" }, "actress": {} } ] } Guest User
{ "cartId": 604638499041, "userAuthToken": cypher, "registeredUser": simulated, "items": [ { "itemId": "1000000015", "quantity": 5, "group": [ "LPCUsIdKqZhjHoA1Ok3tMCsc" ], "price": { "sale": 10, "base": 50, "disbelieve": { "price": 0 }, "currency": "USD" }, "extra": {} }, { "itemId": "1002200074", "quantity": one, "group": [ "3NXSiwNoKbQxe5pbM9hc10lb" ], "price": { "sale": 0, "base": 450, "discount": { "price": 0 }, "currency": "USD" }, "extra": {} } ] } The OMS API provides different endpoints that reverberate dissimilar functionalities. Below are some of the functionalities available:
- Merge invitee cart with user cart
- Get cart by cartId or userId
- Add Ship-To to line items
- Get cart by Transport-To Id
- Apply/Remove Promo
- Create Nib-To records (billing details)
OMS engineering available from e-commerce SaaS vendors like fabric features robust APIs that provide almost limitless functionality. Designing a shopping cart database using them from the ground up may not be the best apply of resources. Nevertheless, if you want to build a shopping cart database from scratch for ane reason or some other, this article should signal you lot in the correct direction.
Is It Better To Add Cart Items In Databse Or Use Session,
Source: https://fabric.inc/blog/shopping-cart-database-design/
Posted by: steinmetzocas1943.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is It Better To Add Cart Items In Databse Or Use Session"
Post a Comment